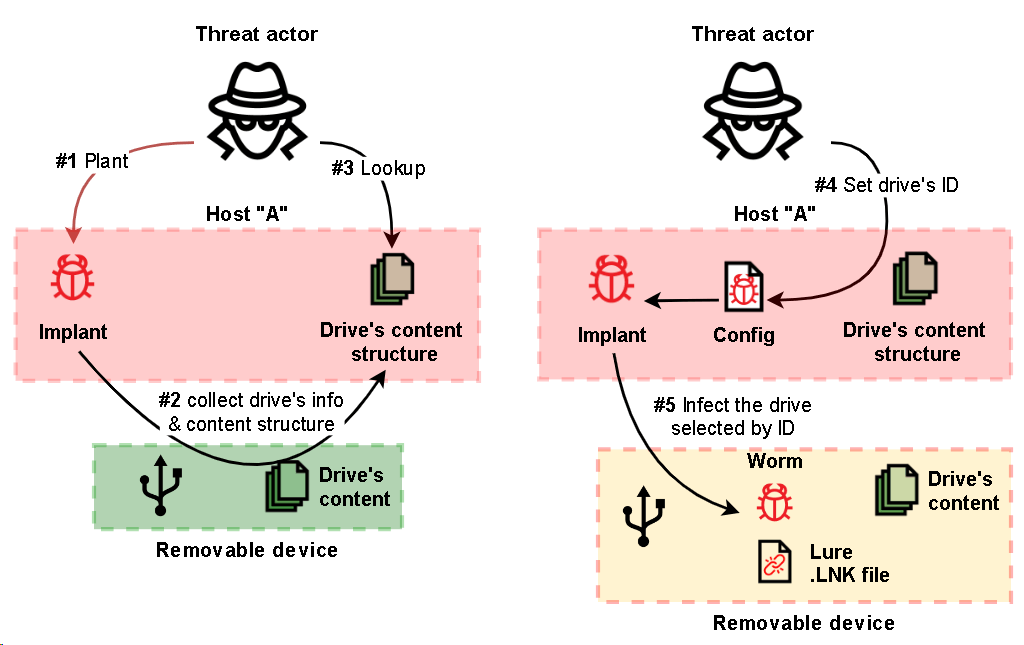
Threat actors targeting the banking and finance industry
Threat actors targeting the banking and finance industry typically have a range of motivations, including financial gain, espionage, and disruption. Here are the key focuses of these actors:
1. Financial Theft and Fraud
- Motivation: Direct monetary gain.
- Techniques:
- Phishing and Spear Phishing: Harvesting customer credentials or employee access.
- Credential Skimming: ATM skimmers and point-of-sale (POS) malware.
- Account Takeover (ATO): Using stolen credentials to drain accounts or commit fraud.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Deceiving employees to approve fraudulent transactions.
2. Ransomware Attacks
- Motivation: Extortion for ransom payments.
- Techniques:
- Encrypting critical data and systems, paralyzing operations.
- Double extortion: Threatening to leak sensitive customer data.
- Targeting backups to ensure ransom payment.
3. Insider Threats
- Motivation: Malicious or inadvertent actions by employees.
- Techniques:
- Misuse of privileged access to steal data or transfer funds.
- Collusion with external cybercriminals.
- Mistakes leading to data breaches (e.g., phishing clicks or poor cybersecurity hygiene).
4. Supply Chain Attacks
- Motivation: Exploiting third-party vulnerabilities to compromise banks indirectly.
- Techniques:
- Targeting fintech partners or vendors.
- Injecting malware into software updates or services.
- Exploiting cloud misconfigurations.
5. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
- Motivation: Espionage or geopolitical disruption.
- Techniques:
- Nation-state actors infiltrating systems for sensitive data.
- Long-term infiltration with undetected lateral movement.
- Zero-day vulnerabilities and sophisticated exploits.
6. Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
- Motivation: Disruption of operations or diversion for other attacks.
- Techniques:
- Overwhelming online banking portals or financial services.
- Using botnets to flood servers and degrade performance.
7. Cryptojacking
- Motivation: Using banking systems to mine cryptocurrencies.
- Techniques:
- Injecting malware to hijack computing resources.
- Targeting internal servers, cloud systems, or customer devices.
8. Data Breaches and Theft
- Motivation: Stealing personally identifiable information (PII) for resale or identity theft.
- Techniques:
- Exploiting vulnerabilities in customer databases.
- Unprotected APIs or insecure mobile banking apps.
- Targeting backups for sensitive data.
9. Emerging Threats (AI and Blockchain Exploits)
- Motivation: Capitalizing on emerging technologies.
- Techniques:
- AI-powered phishing or fraud attempts.
- Exploiting blockchain vulnerabilities in cryptocurrency transactions or smart contracts.
- Deepfakes for BEC or identity theft.
Notable Threat Actor Groups
- FIN7 (Carbanak Group): Specialized in ATM attacks and card fraud.
- Lazarus Group: North Korean APT targeting cryptocurrency and financial institutions.
- Cobalt Group: Focused on ATM jackpotting and SWIFT system attacks.
- TA505: Known for large-scale phishing campaigns and ransomware targeting financial organizations.
Mitigation Strategies
- Zero Trust Architecture: Limiting lateral movement and access to critical systems.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Reducing credential compromise risks.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Collaborating with industry groups (e.g., FS-ISAC).
- Continuous Monitoring: Detecting anomalous behavior in real-time.
- Employee Training: Addressing phishing and social engineering awareness.